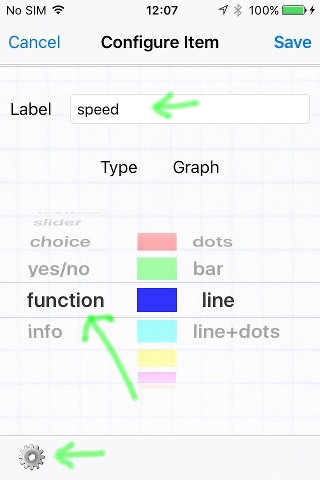
- Give your value a name
- Select 'function' as the type
- Tap the gear icon at the bottom to configure
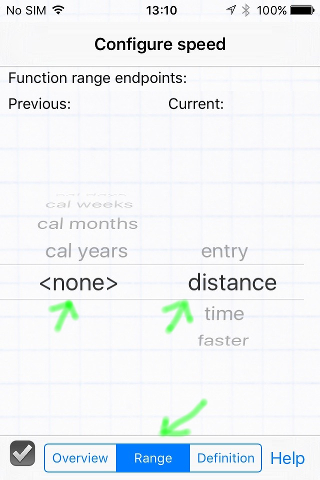
- Select the Range tab to set the endpoints
This function will only use values from the current entry, so set the Previous: endpoint to <none>. Set the Current: endpoint to distance so this result will only be calculated when there is a value in the distance field.
In this case, the function will also not be calculated without a value in the time field as this is recognized as a division by zero.
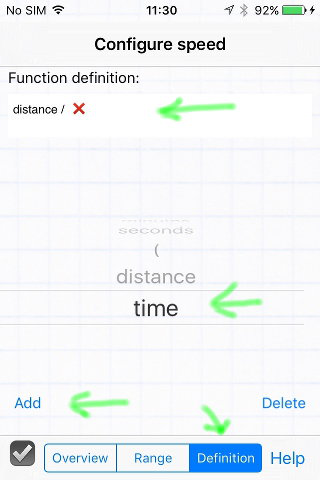
- Select the Definition tab
- Build the function by selecting items from the spinner and tapping the 'add' button
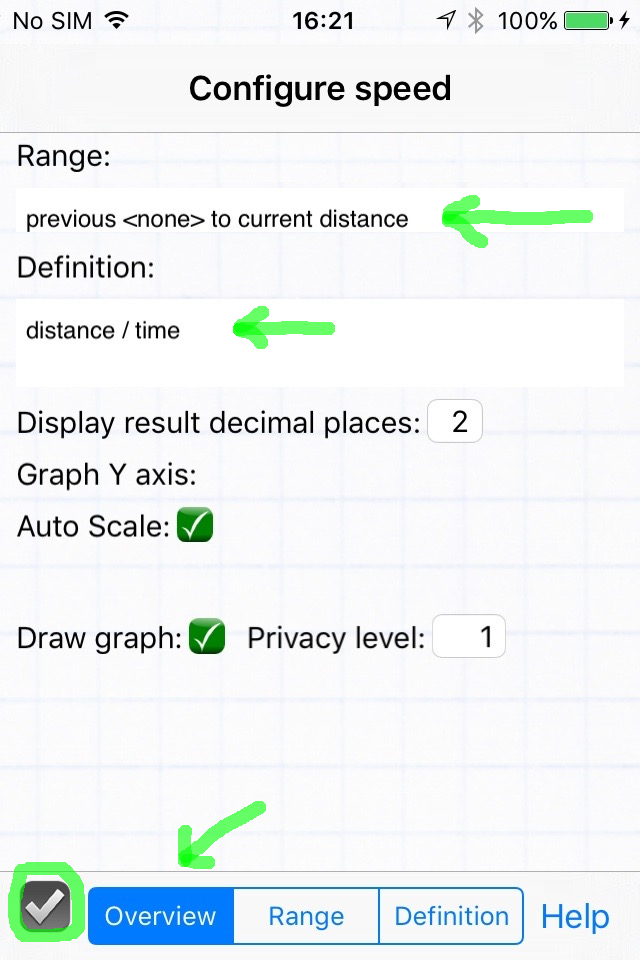
- Select the Overview tab to check your setup
- The range will only be over the values in the current entry (previous <none>), and only when 'distance' has a value.
- The function is 'distance divided by time'
- Tap the checkbox to return
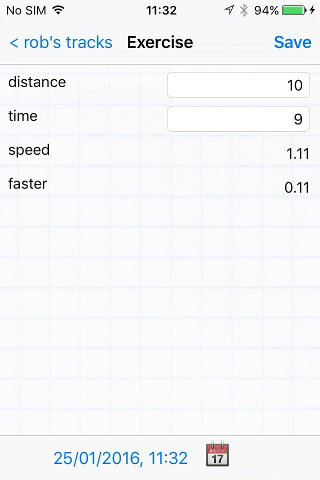
Here's a second function has been defined to use the results of the first.
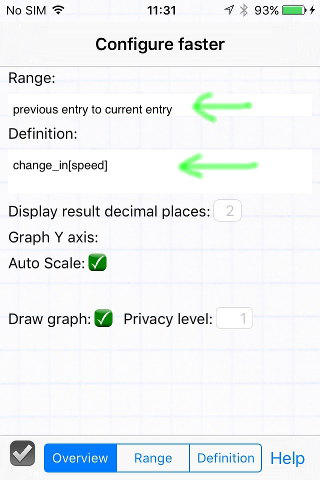
- The range is from the previous entry to the current entry. Most functions will calculate results over several date entries (a.k.a. database records).
- This function is defined to use only the change_in[] operator, which calculates the difference in the specified variable (the speed result from the function above) between the two range endpoints.